MLflow Example
Once you have a Union account, install union:
pip install unionExport the following environment variable to build and push images to your own container registry:
# replace with your registry name
export IMAGE_SPEC_REGISTRY="<your-container-registry>"Then run the following commands to run the workflow:
$ git clone https://github.com/unionai/unionai-examples
$ cd unionai-examples
$ union run --remote <path/to/file.py> <workflow_name> <params>The source code for this example can be found here.
import mlflow.keras
import tensorflow as tfLet’s first import the libraries.
from flytekit import ImageSpec, Resources, task, workflow
from flytekitplugins.mlflow import mlflow_autolog
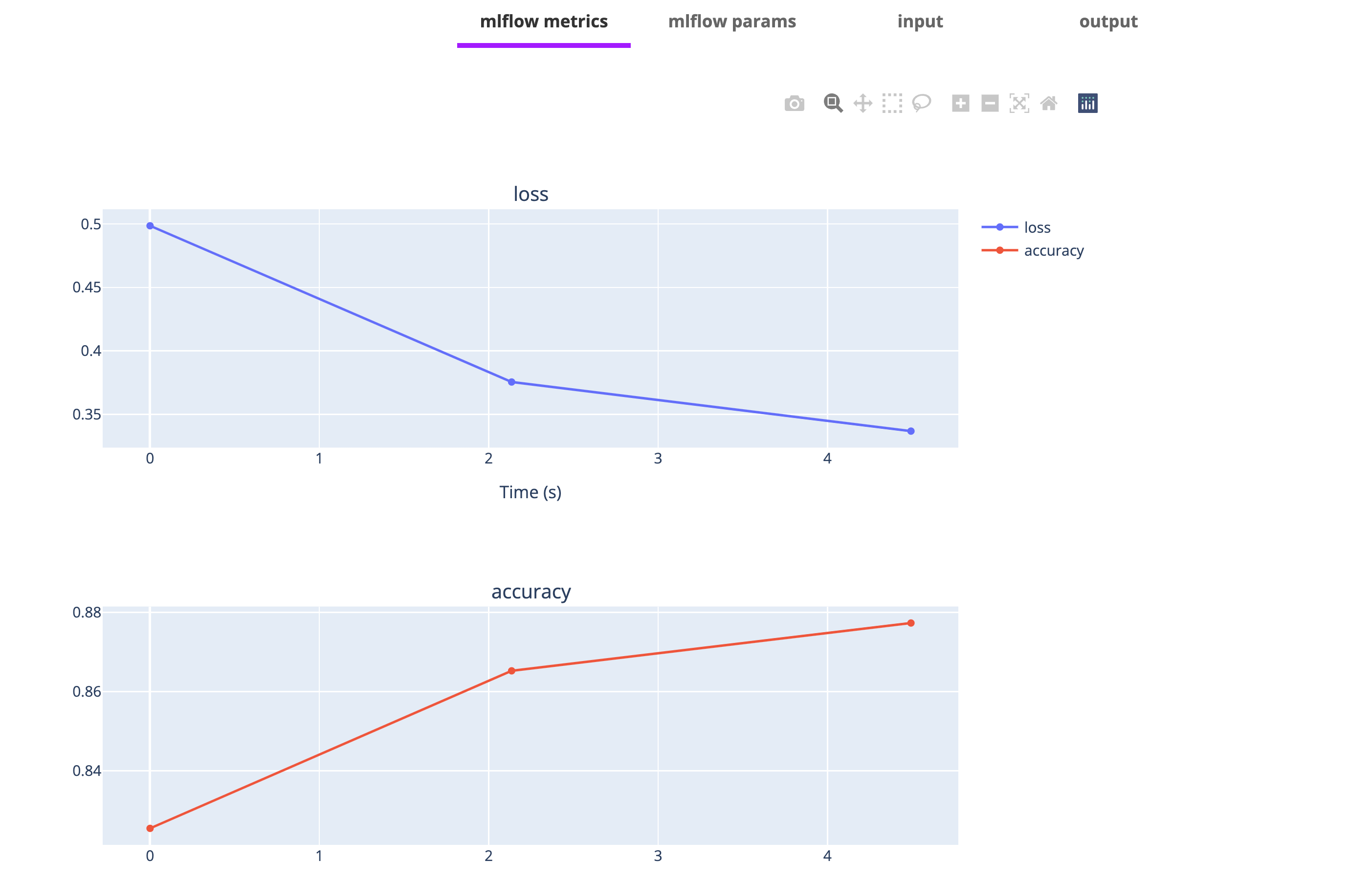
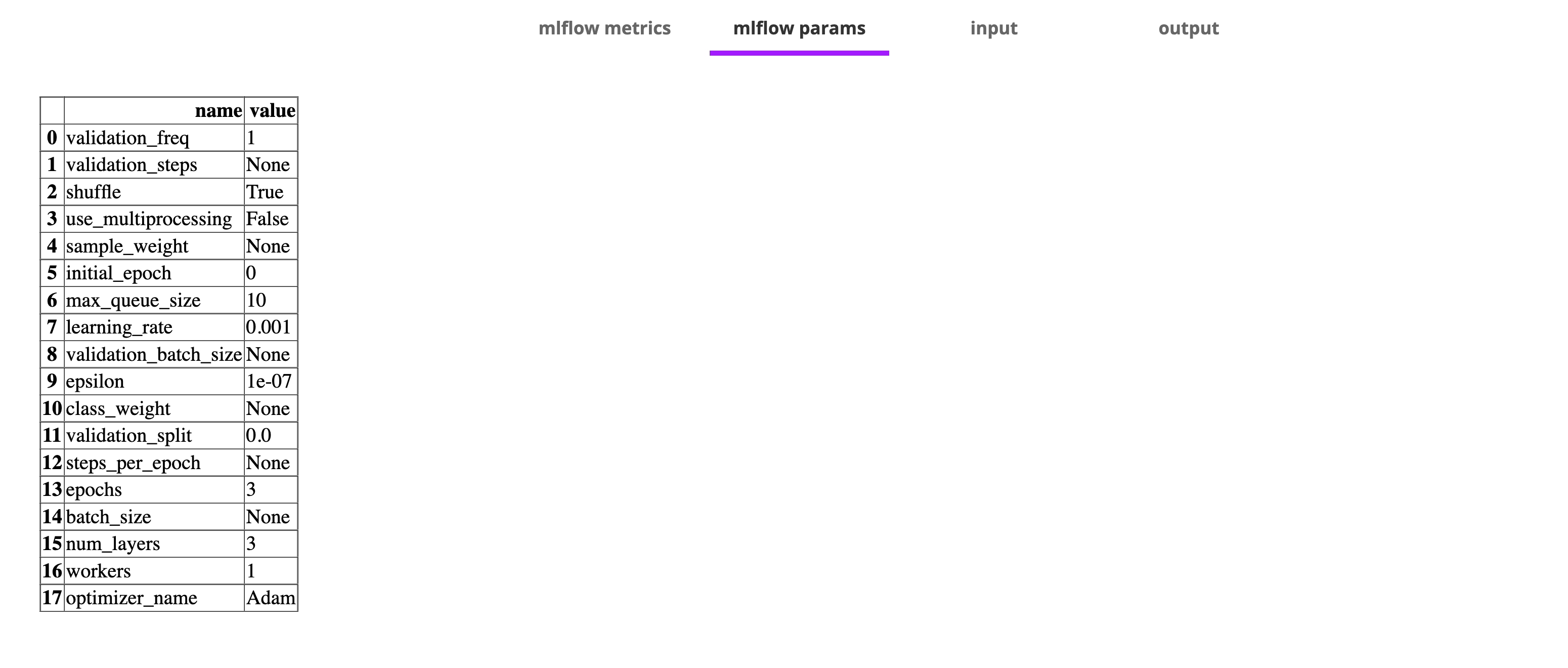
custom_image = ImageSpec(registry="ghcr.io/flyteorg", packages=["flytekitplugins-mlflow", "tensorflow"])Run a model training here and generate metrics and parameters.
Add mlflow_autolog to the task, then flyte will automatically log the metric to the Flyte Deck.
@task(enable_deck=True, container_image=custom_image, requests=Resources(mem="3000Mi"))
@mlflow_autolog(framework=mlflow.keras)
def train_model(epochs: int):
# Refer to https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/keras/classification
fashion_mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(train_images, train_labels), (_, _) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
train_images = train_images / 255.0
model = tf.keras.Sequential(
[
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(128, activation="relu"),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10),
]
)
model.compile(
optimizer="adam",
loss=tf.keras.losses.SparseCategoricalCrossentropy(from_logits=True),
metrics=["accuracy"],
)
model.fit(train_images, train_labels, epochs=epochs)
Finally, we put everything together into a workflow:
@workflow
def ml_pipeline(epochs: int):
train_model(epochs=epochs)
if __name__ == "__main__":
print(f"Running {__file__} main...")
ml_pipeline(epochs=5)